The Inductor is a device that stores electrical energy as magnetic energy. The structure of an inductor is similar to that of a transformer, but with only one winding. An inductor has a certain inductance that only resists changes in current. If the inductor is in a state where no current is flowing through it, it will try to block current from flowing through it when the circuit is closed. If the inductor is in a current state, it will try to maintain the current when the circuit is disconnected. Inductor also known as choke, reactor, dynamic reactor.
Inductors are generally composed of skeleton, winding, shielding cover, packaging material, magnetic or iron core.
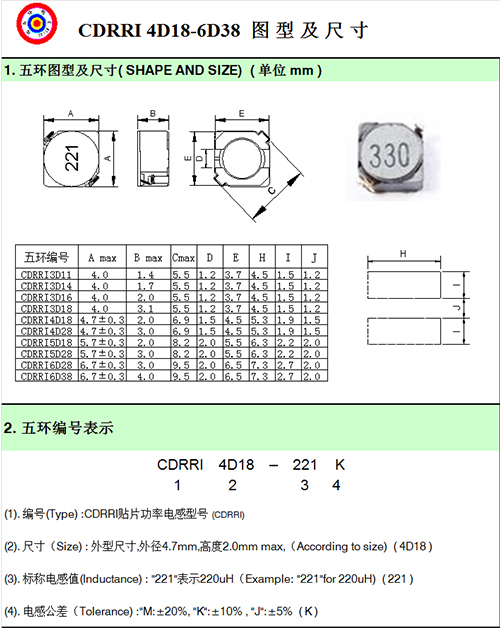
1. Skeleton. Skeleton generally refers to winding coil bracket. Some large volume of fixed inductors or adjustable inductors (such as oscillating coils, flow-blocking coils, etc.), most of them are enameled wire (or gauze wire) around the skeleton, and then the magnetic core or copper core, iron core into the inner cavity of the skeleton, in order to improve its inductance. The skeleton is usually made of plastic, bakelite, ceramic, according to the actual needs that can be made into different shapes. Small inductors (such as color code inductors) typically do not use a skeleton, but instead wrap enameled wire directly around the core. Hollow inductors (also known as boxed coils or hollow coils, often used in high frequency circuits) do not use magnetic cores, skeletons and shields, etc. Instead, they are first wound on the mold and then removed from the mold, and the coils are separated from each other by a certain distance.
2. Winding. A winding is a group of coils with a specified function, which is the basic component of an inductor. The windings are single and multilayer. The single-layer winding also has two forms: close winding (winding conductors one by one) and inter-winding (winding conductors in each circle are separated by a certain distance). The multilayer winding has many kinds of winding methods, such as layering flat winding, random winding and honeycomb winding.
3. Magnetic core and magnetic bar. Magnetic core and magnetic bar generally use nickel zinc ferrite (NX series) or manganese zinc ferrite (MX series) and other materials, it has "work" shape, column shape, cap shape, "E" shape, can shape and other shapes.
4. Iron core. Iron core materials are mainly silicon steel sheet, permo alloy, etc., its shape is mostly "E" type.
5. Shielding cover. In order to avoid the magnetic field generated by some inductors at work affecting the normal work of other circuits and components, a metal screen cover is added (such as the oscillating coil of a semiconductor radio, etc.). The inductor with a shield will increase the coil loss and reduce the Q value.
6. Packaging materials. Some inductors (such as color code inductor, color ring inductor, etc.) after winding, sealing coil and magnetic core with packaging materials. Packaging materials are made of plastic or epoxy resin.
Copper Coil
Inductance is the ratio of the magnetic flux in a wire to the current producing the alternating flux around the inside of the wire when an alternating current is flowing through it. When dc current passes through the inductor, only fixed magnetic field lines are present around it, which does not change with time.
But when an alternating current passes through a coil, it is surrounded by magnetic field lines that change over time. According to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, magnetic generation, the changing magnetic field lines will generate an induced potential at both ends of the coil, which is equivalent to a "new power source". This induced potential generates an induced current when a closed loop is formed. Lenz's law knows that the total amount of magnetic lines of force produced by an induced current should try to prevent the change of magnetic lines of force. The change of magnetic force line comes from the change of external alternating power supply, so from the objective effect, the inductance coil has the characteristic of preventing the current change in ac circuit. The inductance coil has a characteristic similar to the inertia in mechanics, which is called "self-induction" in electricity. Usually, sparks will occur at the moment when the knife switch is opened or switched on. This self-induction phenomenon is caused by high induction potential.
In short, when the inductance coil is connected to the AC power supply, the magnetic field lines inside the coil will change with the alternating current, causing the coil to produce electromagnetic induction. This electromotive force due to the change in the current of the coil itself is called "self-induced electromotive force". It can be seen that the inductance is only a parameter related to the coil number, size and shape and medium, it is the measurement of the inductance coil inertia and has nothing to do with the applied current.
|
|
CDRRI3D11-3D28 Series Features |
|
|||||||||||
|
The five rings number |
L |
DC Resistance mΩ max direct current resistance |
Rated DC Current(A) max |
||||||||||
|
Part No |
u H |
||||||||||||
|
inductance |
3D11 |
3D14 |
3D16 |
3D28 |
|
|
3D11 |
3D14 |
3D16 |
3D28 |
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-1R5N |
1.5 |
|
76 |
52 |
|
|
|
|
2.6 |
1.55 |
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 2R2N |
2.2 |
|
|
72 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.20 |
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-2R4N |
2.4 |
|
129 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 2R7N |
2.7 |
105 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.53 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-3R2N |
3.2 |
|
139 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.80 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 3R3N |
3.3 |
|
|
85 |
72.1 |
|
|
|
|
1.10 |
2.2 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-4R7N |
4.7 |
156 |
214 |
105 |
88.3 |
|
|
0.40 |
1.45 |
0.90 |
1.65 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 6R8N |
6.8 |
225 |
290 |
170 |
119 |
|
|
0.34 |
1.20 |
0.73 |
1.24 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-8R2N |
8.2 |
294 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 100N |
10.0 |
338 |
440 |
210 |
145 |
|
|
0.28 |
1.00 |
0.55 |
1.05 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-120N |
12.0 |
418 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 150N |
15.0 |
550 |
650 |
295 |
213 |
|
|
0.23 |
0.80 |
0.45 |
0.9 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-180N |
18.0 |
626 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 220N |
22.0 |
731 |
830 |
430 |
335 |
|
|
0.19 |
0.65 |
0.40 |
0.76 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-330N |
33.0 |
1108 |
|
675 |
481 |
|
|
0.17 |
|
0.32 |
0.58 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 390N |
39.0 |
1390 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 470N |
47.0 |
|
|
|
599 |
|
|
0.14 |
|
|
0.48 |
|
|
|
|
CDRRI4D18-6D38 Series Features |
|
|||||||||||
|
The five rings number |
L |
DC Resistance mΩ max direct current resistance |
Rated DC Current(A) max |
||||||||||
|
Part No |
u H |
||||||||||||
|
inductance |
4D18 |
4D28 |
5D18 |
5D28 |
6D28 |
6D38 |
4D18 |
4D28 |
5D18 |
5D28 |
6D28 |
6D38 |
|
|
CDRRIXXX-1R0N |
1.0 |
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.72 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 1R2N |
1.2 |
|
23.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.56 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-1R8N |
1.8 |
|
27.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 2R2N |
2.2 |
75 |
31.3 |
|
|
|
|
1.32 |
2.04 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-2R6N |
2.6 |
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.6 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 2R7N |
2.7 |
105 |
43.3 |
|
|
|
|
1.28 |
1.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-3R0N |
3.0 |
|
|
|
24 |
24 |
|
|
|
|
2.4 |
3.0 |
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 3R3N |
3.3 |
110 |
49.2 |
|
|
|
20 |
1.04 |
1.57 |
|
|
|
3.5 |
|
CDRRIXXX-3R9N |
3.9 |
155 |
64.8 |
|
|
27 |
|
0.88 |
1.44 |
|
|
2.6 |
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 4R1N |
4.1 |
|
|
57 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.95 |
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-4R2N |
4.2 |
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.2 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 4R7N |
4.7 |
162 |
72 |
|
|
|
|
0.84 |
1.32 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-5R0N |
5 |
|
|
|
|
31 |
24 |
|
|
|
|
2.4 |
2.9 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 5R3N |
5.3 |
|
|
|
38 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.9 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-5R4N |
5.4 |
|
|
76 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.60 |
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 5R6N |
5.6 |
170 |
100.9 |
|
|
|
|
0.8 |
1.17 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-6R0N |
6 |
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.25 |
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 6R2N |
6.2 |
|
|
96 |
45 |
|
27 |
|
|
1.40 |
1.8 |
|
2.5 |
|
CDRRIXXX-6R8N |
6.8 |
200 |
108.9 |
|
|
|
|
0.76 |
1.12 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 7R3N |
7.3 |
|
|
|
|
54 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.1 |
|
|
CDRRIXXX-7R4N |
7.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.3 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 8R2N |
8.2 |
245 |
117.5 |
|
53 |
|
|
0.68 |
1.04 |
|
1.6 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-8R6N |
8.6 |
|
|
|
|
58 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.85 |
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 8R7N |
8.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.2 |
|
CDRRIXXX-8R9N |
8.9 |
|
|
116 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.25 |
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 100N |
10 |
200 |
128.3 |
124 |
65 |
65 |
38 |
0.61 |
1.0 |
1.20 |
1.30 |
1.7 |
2.0 |
|
CDRRIXXX-120N |
12 |
210 |
131.6 |
153 |
76 |
70 |
53 |
0.56 |
0.84 |
1.10 |
1.20 |
1.55 |
1.7 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 150N |
15 |
240 |
149 |
196 |
103 |
84 |
57 |
0.50 |
0.76 |
0.97 |
1.10 |
1.4 |
1.6 |
|
CDRRIXXX-180N |
18 |
338 |
166 |
210 |
110 |
95 |
92 |
0.48 |
0.72 |
0.85 |
1.00 |
1.32 |
1.5 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 220N |
22 |
397 |
235 |
290 |
122 |
128 |
96 |
0.41 |
0.7 |
0.80 |
0.90 |
1.2 |
1.3 |
|
CDRRIXXX-270N |
27 |
441 |
261 |
330 |
175 |
142 |
109 |
0.35 |
0.58 |
0.75 |
0.85 |
1.05 |
1.2 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 330N |
33 |
694 |
378 |
386 |
189 |
165 |
124 |
0.32 |
0.56 |
0.65 |
0.75 |
0.97 |
1.1 |
|
CDRRIXXX-390N |
39 |
709 |
383.7 |
520 |
212 |
210 |
138 |
0.30 |
0.50 |
0.57 |
0.70 |
0.86 |
1.0 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 470N |
47 |
|
587 |
595 |
260 |
238 |
155 |
|
0.48 |
0.54 |
0.62 |
0.8 |
0.95 |
|
CDRRIXXX-560N |
56 |
|
624.5 |
665 |
305 |
277 |
202 |
|
0.4 |
0.5 |
0.58 |
0.73 |
0.9 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 680N |
68 |
|
699 |
840 |
355 |
304 |
234 |
|
0.35 |
0.43 |
0.52 |
0.65 |
0.75 |
|
CDRRIXXX-820N |
82 |
|
914.8 |
978 |
463 |
390 |
324 |
|
0.32 |
0.41 |
|
0.6 |
0.7 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 101N |
100 |
|
1020 |
1200 |
520 |
535 |
358 |
|
0.29 |
0.36 |
0.42 |
0.54 |
0.65 |
|
CDRRIXXX-121N |
120 |
|
1270 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.27 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 151N |
150 |
|
1350 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.24 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-181N |
180 |
|
1540 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.22 |
|
|
|
|